High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) pipes have increasingly replaced metal, concrete, and PVC pipes in various sectors due to their durability, lightweight nature, long lifespan, and flexibility. Key applications include:
Agricultural irrigation systems
Urban and rural infrastructure
Natural gas transmission lines
Mining and tunneling operations
Marine pipelines
Fire suppression systems
The HDPE pipe market is expected to grow at an annual rate of 5%, reaching $26.518 billion by 2025. Notably, over 90% of gas pipeline networks in Europe and 95% of plastic piping in the United States are made from polyethylene. As a result, the study of failure mechanisms and lifespan prediction of PE pipes remains a major concern for manufacturers and network operators.
The creep rupture behavior of polyethylene pipes is time- and temperature-dependent and is typically represented by a long-term failure curve divided into three phases:
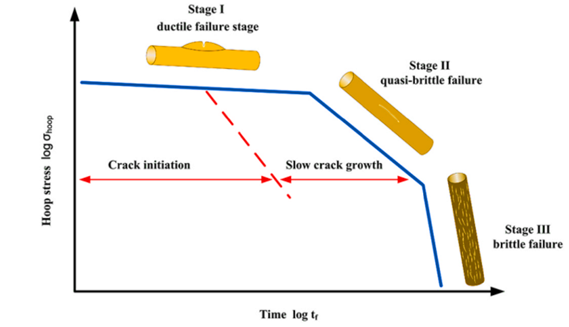
Phase I: Ductile failure
Phase II: Quasi-brittle failure
Phase III: Brittle failure
In general, ductile failure indicates a shorter lifespan, while brittle failure suggests a longer service life. The minimum acceptable lifespan for polyethylene pipes is considered to be 50 years. The transition from ductile to brittle failure takes considerable time, and identifying the mechanical knee point is often challenging.
In the quasi-brittle phase, pipe failure is mainly due to Slow Crack Growth (SCG), whereas in the brittle phase, degradation is primarily caused by stress-independent aging. SCG is the leading cause of final failure in polyethylene applications and accounts for approximately 15% of sudden failures in polymeric materials. It is an intrinsic property influenced by raw material composition and injection molding processes, and is further affected by external factors such as stress, temperature, surfactants, and the structural integrity of the material. When polyethylene is subjected to mechanical stress and exposed to aggressive environments, the SCG process accelerates significantly.
Polyethylene pipe definition, polyethylene pipe applications, advantages of polyethylene pipes, defects in polyethylene pipes, pipe lifespan, slow crack growth
If you'd like, I can help you turn this into a formal article, a brochure, or even a presentation. Just say the word!